🇮🇳 India | 🇺🇸 USA | 🇫🇷 France | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 🇦🇪 UAE
🇮🇳 India | 🇺🇸 USA | 🇫🇷 France | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 🇦🇪 UAE
🇮🇳 India | 🇺🇸 USA | 🇫🇷 France | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 🇦🇪 UAE
🇮🇳 India | 🇺🇸 USA | 🇫🇷 France | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 🇦🇪 UAE
12 Months
Mode: 💻Online| 🕒Self-paced| 📲 Live | 🧘♀️Group Yoga

For International Students –
USD 1020

For Indian Students –
INR 60,000
1 Year 800 – hour Advanced Yoga Therapy Course
 Prevent degenerative arthritis, joint pain by preventing cartilage and joint breakdown
Prevent degenerative arthritis, joint pain by preventing cartilage and joint breakdown
 Increases immunity by increasing the drainage of lymph and destroying cancerous cells and toxic waste products
Increases immunity by increasing the drainage of lymph and destroying cancerous cells and toxic waste products
 Reduces high blood pressure by Shavasana like relaxation yogic techniques within three months
Reduces high blood pressure by Shavasana like relaxation yogic techniques within three months
 Lowers insulin resistance, lowers blood sugar and LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and prevents diabetes
Lowers insulin resistance, lowers blood sugar and LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and prevents diabetes
 Reduces anxiety by lowering levels of stress-hormone cortisol and improving mood
Reduces anxiety by lowering levels of stress-hormone cortisol and improving mood
 Regular yoga practice improves memory, coordination, reaction time and even IQ scores
Regular yoga practice improves memory, coordination, reaction time and even IQ scores
 Improves lung functions and fights respiratory diseases
Improves lung functions and fights respiratory diseases
Duration : 12 Months
Contact hours: 100 hours Direct: 120 hours, Indirect hours: 680 hours
Time commitment (hours per week) 8-10 hours
Pace (weekly): Once
Session (hours): Once a week
Skill level: Advanced, Basic Yoga Therapy, YCB Level 2 certified/ 400 hours TTC yoga trainers eligible
Language: English
Syllabus: Yoga Therapy TTC (Level 2) Full Syllabus (click here to check syllabus)
Maximum group size: 8
Course Pricing:
Indian Students – INR 60,000
Intl. Students – USD 1020 ( Including YCB Assessment Fees of 450 USD)
1. Name of the Certification: Yoga Therapist (YTh)
2. Requirement/ Eligibility:
a. For open candidates there is no eligibility criteria
b. Any Degree holder
3. Brief Role Description: Can work along with certified physician or certified Yoga
Consultant to give Yoga Therapy on all disorders
4. Minimum age: No age limit
5. Personal Attributes: The job requires individual to have Good communication skills,
time management and ability to understand the body language of the trainees. The job
requires individual to possess key qualities such as self discipline, confidence, maturity,
patience, compassion, active listening, time management, empathy, language
proficiency, ability to build caring relationships, friendly and approachable, credibility
etc.
6. Credit points for certificate: 46 credits
7. Duration of course: Not less than 800 hours (Contact program for 100 hrs. to be
conducted on Anatomy, Physiology).
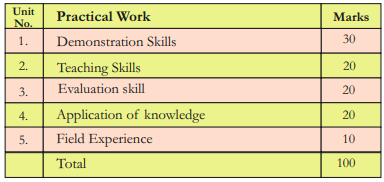
8. Mark Distribution: Total Marks: 200 (Theory:100+Practical: 100)
UNIT 1 Yoga and Human Body
A. Anatomy & Physiology:
1.1 Musculo-Skeletal System : Muscle – Classification – Histology – properties of each type – distribution – Mechanism of muscle contraction (Brief) – neuromuscular transmission (Brief), ligaments, tendons, Skeleton-Bones-types, Structure & function, Spinal column. Joints – Types, Structure, Functions.
1.2 Blood and Immune System: Composition of blood corpuscles – R.B.C., W.B.C., Platelets. Plasma, Hemoglobin – Coagulation of blood and anticoagulants. Blood groups and its importance, lymphatic system , Immunity – types & mechanism.
1.3 Cardiovascular system: Anatomy of Heart and blood vessels – -Innervations’ of heart – Properties of cardiac muscle – Control of cardiac cycle and circulation – Cardiac output – Blood pressure.
1.4 Respiratory System: Anatomy-Gross & Histological – Mechanism of Breathing, Exchange of gases Pulmonary function tests-lung volumes – Control of respiration.
1.5 Digestive system: Anatomy – Gross and Histological – Mechanism of secretion of – Saliva, Gastric Juice, Pancreatic Juice, Bile, Intestinal secretion – Role of these secretions in digestion of food, Absorption and assimilation and formation of faces.
1.6 Excretory System and temperature regulation: Anatomy-Gross & Histology – Functions of glomerule and renal tubules Micturition and composition of urine – structure and functions of skin-Regulation of body temperature.
1.7 Endocrine System : Anatomy – Gross & Histological, Thyroid, Parathyroid, Supra – renal, Pituitary, Islets of Langerhans – Function of thyroid and parathyroid hormone, effect of hypo and hyperactivity on the body. Hormones of supra-renal and their action and effect of hypo & hyper activity on the body. Hormones of pituitary gland- its action and effect of hypo & hyper activity on the body. Role of insulin in glucose metabolism.
1.8 Special senses : Eyes Anatomy – Histology of retina, Corneal function, Physiology of vision & accommodation, Sense of smell – nasal mucosa, tongue, taste buds. Ear-Mechanism of hearing and function of semicircular canal.
1.9 Reproductive System: Anatomy – Gross & History of Male reproductive system – Spermatogenesis. Female reproductive system – Ovarian harmones, Menstruation, Pregnancy, Parturition, Lactation.
1.10 Nervous System : Anatomy – Gross – Cerebrum, cerebellum, Spinal cord. Histology – Nerve – structure and properties of neurons – Nerve – Action Potential – generation propagation – factors influencing. Classification of neurons and nerve fibers Receptors and reflex arc. Functions and important connections of Cerebrum, Pons, Medulla, Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Cerebellum – Autonomic nervous system – Sympathetic and parasympathetic – anatomy & functions.
1.11 Homeostasis: The concept of homeostasis, Homeostasis, Regulatory systems of the body, Characteristics of control systems, Physiological basis of mind-body intervention.
B. Anatomy & Physiology:
Study of – cognitive processes. Higher mental processes, feeling and emotion, mental abilities and personality. A comparative study of total personality according to Yoga and Modern Psychology. Its Meaning, definition and nature of consciousness as described in Vedas, Upanishads, Bhagwad Gita, Yogasutra and Yogavashishtha; Spiritual and scientific approach to human consciousness. Yogic Method of elevation of human consciousness: Bhaktiyoga, Jnanyoga, Karmayoga, Mantrayoga, Ashtangayoga, Hathayoga.
C. Yoga and Diet:
Concept and types of diet in Traditional Yogic Texts; Concept of food and Nutrition and its components,concept of Health and Malnutrition, Assessment of Nutritional status, knowledge of Therapeutic Modifications of Normal Diet, Preparation of Therapeutic charts for special groups/patients, Role of Yogic diet in health and disease.
UNIT 2 Fundamental Principles of Yoga Therapy
2.1 Concept of Yoga and Health in Indian Traditional Systems of Medicine i.e. Ayurveda, Naturopathy and Siddha Systems of Medicine, Utility and Limitations of these systems in relation to Yoga and health.
2.2 Yogic Concept of Health: Meaning and definitions, Concept of Adhi and Vyadhi, Role of Yoga in preventive health care – Heyamdukhamanagatam Tapatrayas , Kleshas and Anatryas.
2.3 Concepts of Trigunas, Pancha-mahabhutas, Pancha-prana and Pancha Koshas.
2.4 Role of Yogic Positive Attitudes (Maitri, Karuna, Mudita and Upeksha) for Healthy Living, Concept of Bhavas and Bhavanas with its relevance in Health and well-being.
2.5 Concept of Aahara, Vihara, Aachara and Vichara.
2.6 Role of Shuddhi Prakriyas in preventive, promotive and curative aspects of Yoga Therapy -Health, Karma Shuddhi (Yama, Niyama), Ghata Shuddhi (Shatkarma), Snayu Shuddhi (Asana), Prana Shuddhi (Pranayama), Indriya and Mano Shuddhi (Pratyahara), Mana, Buddhi, Ahamkar and ChittaShuddhi (Dharana, Dhyana and Samadhi).
UNIT 3 Application of Yoga Therapy in Traditional Yoga Texts
3.1 Bhagvadgita : Definitions of Yoga in Bhagavadgita and their relevance in Yoga therapy, Concept of Samkhya Yoga in Bhagavadgita ,Significance of Bhagavadgita as a synthesis of Yoga, Concept of Sthita Prajna, stages and characteristic of it. Concept of Atman (Purusha) and Jivatman in Bhagavadgita. Concept of Paramatman (Parmeshwar or Purushottam) as described in Bhagavadgita, Concept of world (Jagat, Samsar) as described in Bhagavadgita, Psychotherapy concept of Bhagavadgita in various mental disorders like depression, anxiety etc, Significance of Yogasadhana, Karmayoga, Jnana Yoga, YOG Certification Board 4 Dhyana Yoga and Bhakti Yoga in Bhagavadgita, Concept and classification of Ahara and and its role in Adhyatma Sadhana as described in Bhagavadgita, Concept of Triguna in the context of Bhagavadgita, Importance of of Bhagavadgita in day to day life.
3.2 Patanjala Yoga Sutra: Applications and Understanding of Patanjala Yoga & Personality Development. The nature of seer in pure state, Concept of Vrttis – Nature, classification, definition, method to control of chittavrttis (Abhyasa and Vairagya), Ishwarapranidhana– a means to attain Samadhi, Definition & quality of Ishwara ; Chittavikshepa, Chittaprasadana and its associates, Samadhi and its classification, Sabijasamadhi, Speciality of Nirvichara, Rthambaraprajna, Nirbijasamadhi; Significance of Samyama and its applications, Parinamavad, Dharma and Dharmi, Parinamanyateva, Samyama on – Parinamatraya, knowledge of bhutaruta, Parachittajnana, Antardhana. Aparantajnana, Samyama on – Maitri, Surya, Chandra, Nabhichakra, Kanthakupa, Kaurmanadi, Murdhajyothi, Pratibha, Hrdaya, Swartha, Udana, Samana, and their benefits. Attainments of divyashrotra, Akashagamana, Bhutajaya, Animadi siddhi, Indriyajaya, Kaya jaya, Sarvajnatva, Concept of Kaivalya in Patanjali Yoga Sutra, Kaivalya–Introduction, Siddhi, Jatyantaraparinama, Nirmanachitta.Karma, Vasana, Smriti and Samskara
3.3 Yoga Vashishtha: Concept of Yoga: Introduction and Highlights of Yoga Vasishtha, Definitions of Yoga and their relevance in Yoga Vasishtha; Concept of Mind: World is the projection of Mind; Manah Prashamanah upayah Yoga: Mind control through abhyasa ( practice) and vairagya (detachment); Concept of Jnana: Jnana Saptabhumika, importance of knowledge and types of knowledge, Management of Mind and emotions-enhancing the power of discrimination (Viveka); Prana and Pranayama: Control of breathing; the story of Kakabhushanda, Understanding of the Concept of Adhi and Vyadhi; concept of Prana & Pranayama; Concept of Samadhi and Moksha: Good Association; Self Enquiry; Development of Satvaguna (Good virtues), Eight Limbs of Meditation.
UNIT 4 Physiological And Psychological Effects Of Hatha Yoga Practices
4.1 Shatkriyas and Sthula and Sukhsamvyayam Kriya: Physiological benefits of sthula and sukhsamvyayam on human body in preparation of yogic practice. Knowledge of sthula and sukhshmavyayam for different parts of the body; An overview of diffusion, osmosis, active transport across cell membrane; significance of using salt during the practice of shatkriya; Tonicity of the solution such as hypotonic, hyper tonic and isotonic solution and the impact of the same on physiology; Effects of kriya on GIT and Respiratory physiology; peristalsis and mechanism of action, Effect of Kriyas in encouraging the peristalsis; Opening and closing of sphincter; Role of Kriyas in smooth operation of sphincter ; Mechanism of action of Kriya practices in the activation of vagus nerve, effect of Kriyas on gastric mucosa on digestive system; YOG Certification Board 5 Development of negative pressure and the impact of sustenance of the negative pressure in body physiology.
4.2 Asana: Physiology of exercise, Asana – Types and Categories; Musclulo skeletal system and mechanisms involved; Effect of Yogic practices in setting up the internal environment of the body, Mechanical influence of Yogasana; Psychosomatic mechanism; Mechanism of influence of six types of Yogasanas: stretching; pivoting; strengthening; inverted; pressing; equilibration, Reciprocal inhibition and innervations; Concept of energy expenditure and role of asana practice on energy expenditure.
4.3 Pranayama: Mechanism of respiratory system and gas exchange, Regulation of respiration, Psycho- physiological effect of Pranayama: changing of ratio of oxygen and carbonic carbon–dioxide in our body; enabling different groups of muscles in breathing; Pranayama as respiratory pump; Reflex impact over sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system; Role of Pranayama on lung function test. Role of Pranayama and other Yoga practices on compliance, Ventilation perfusion ratio, alveolar ventilation, dead space volume and minute ventilation, Neurophysiological mechanism of Kevala, Antar and Bahirkumbhaka.
4.4 Meditation: Different types of meditation its impacts on central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. Different types of meditation its impacts on cardiovascular system, respiratory system, nerve – muscle physiology. Meditation its impacts on relaxation of each and every system of body.
4.5 Mudra and Bandhas: Nerve reflexes; Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation; Effect of Bandhas on joint complexes; Central bandhas and co activation of opposing muscles in spinal joint complexes; Jalandharabandha effects neck joint complexes; Uddiyanbandha effects upper joint complexes; and Moolabandha for lower back joint complexes; Isometric muscle activation and Bandhas; Synergistic muscle activation during Bandha practices; Navadvara and their significance in yoga; Principles behind the practice of Mudras; Resting membrane potential; transmission of nerve impulse; significance of Neuro psychological lock and its impulse in body physiology; secretion of neurotransmitter in the brain; Role of mudra and its physiological functions of the body.
UNIT 1 Demonstrative Skills
1.1 Recitation of Hymns and Mantras Ÿ Concept and Brief introduction to Pranav and hymns Ÿ Recitation of Pranav and Soham japa Ÿ Recitation of Pratah-smaran, Dhyana mantra, Pranayama Mantra, Asana Mantra, Shanti Mantras. .
1.2 Shatkarmas: Demonstrating ability of preforming shatkarma (Cleansing Process) Ÿ Vamandhauti, Vastradhauti, Dandadhauti , Ÿ Neti (Sutra and Jal ), Ÿ Kapalbhati, Agnisara, Ÿ Nauli. Ÿ Laghooand Poornasankhaprakshalana,
1.3 Sukshma Vyayama, Sthula Vyayama and Suryanamaskar Ÿ Ucharan-sthal-tathtavishudhichakrashudhi Ÿ Budhitathadritishakivikasaka Ÿ Medhashaktivikasaka Ÿ Kapolshaktivikasaka Ÿ Grivashakti vikasak Ÿ Vakshasthalshaktivikasaka (i and ii) Ÿ Katishaktivikasaka (i,ii,iv,v) Ÿ Janghaskativikasaka (i,ii) Ÿ Pindalishkativikasaka Ÿ Hridgati and sarvangpushti. Ÿ Yogic Surya Namaskar of BSY, Swami Dhirendra Brahmachari and its Variations.
1.4 Yogasanas Ÿ Standing Yogasana: Tadasana, Ardhchakrasana, Vrikshasana, Padahastasana, Veerbhadrasana and its variations, Garudasana, Parivrittatrikonasana, Parshakonasana. Ÿ Sitting Yogasana: Paschimottanasana, Vajrasana, Suptavajrasana, Vakrasana, Gomukhasna, Marichyasana, Ardhamatsyendrasana, Uttanmandukasana, Sasakasana, Ustrasana, Dandasana, Mandukasana, Kurmasana, Kukkutasana, Bhadrasana Ÿ Prone lying Yogasana: Makarasana, Bhujangasana, Salabhasana, Dhanurasana Ÿ Supine lying Yogasana: Uttanapadasana, Ardhahalasana, Halasana, Chakrasana, Saral Matsyasana, Matsyasana ,Pawanmuktasana and its variations, Naukasana, Shavasana, Setubandhasana, Sarvangasana Ÿ Topsy Turvy Yogasana: Sirshasna and its variation.
1.5 Pranayama: Knowledge and Demonstrated ability to perform the following practices Ÿ Breath awareness Ÿ Sectional breathing, Ÿ Anuloma Vilom Ÿ Nadishodhana Pranayama. SuryaBhedi and Chandrabhedi Pranayama Ÿ Ujjayi pranayama and Bhastrika pranayama Ÿ Seetali Pranayama and Sitali Pranayama YOG Certification Board 7
1.6 Meditation: Knowledge and Demonstrated ability to Heal at the Physical Level, Mental level, Prana Level and Conscious level with below mentioned practices. Ÿ Antarmaun Ÿ Ajapa japa Ÿ Yoga Nidra Ÿ Dharna Ÿ Om Meditation, Vipasana and prekshadhyana
1.7 Bandhas and Mudras: Knowledge and Demonstrated ability to perform following practices:- Ÿ Jalandhara bandha, uddiyana bandha and mool bandha, Mahabandha. Ÿ Mahamudra, Bhairavi mudra,Yoni mudra,shambhavi mudra and shandmukhi mudra.
1.8 Yogic Counseling: Introduction to counselling, nature approaches and challenges; Approach to counselling- Attitude change towards Yoga through individualized counselling, Psychological & yogic method Tackling ill effects of conflict and Frustration; Yogic methods Yoga Psychology for Adjustment: Psychological, philosophical and Yogic counselling; the remedial measures; Action in relaxation-the secret of Karma Yoga; Psycho-physiological effects and health benefits of Pranayama, Shatkarma; Bandha and Mudra ; Psychophysiological effects and health benefits of Meditation.
UNIT 2 Therapeutic Skills- Yogic Therapeutic management for various disorders
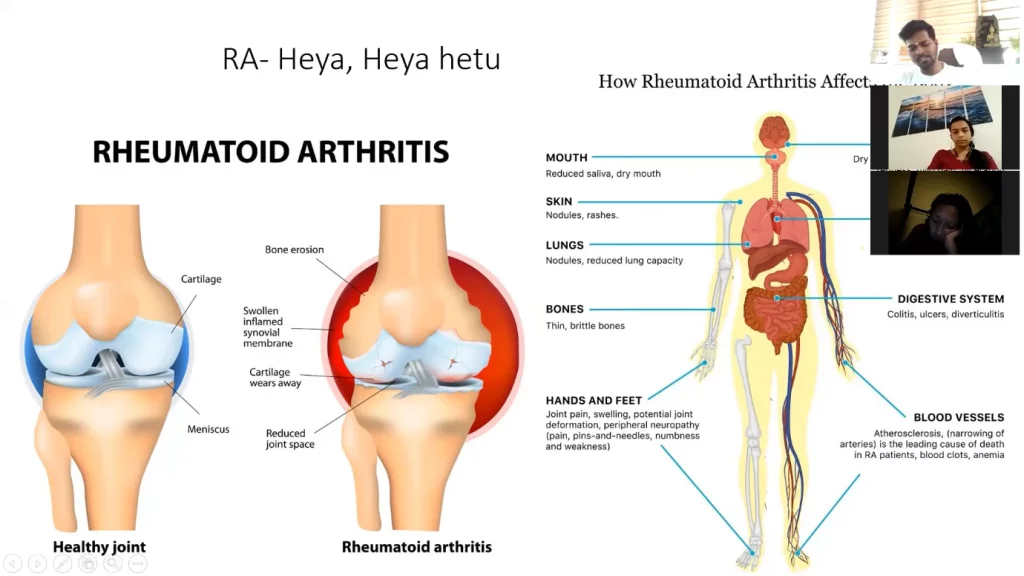
2.1 Role of Yoga practices on various Musculo-Skeletal disorders like Back Pain, Neck pain, Arthritis, Fibromyalgia and Muscular dystrophy; Role of Yogic Diet on Musculo-Skeletal Disorders
2.2 Role of Yoga practices on various Respiratory Disorders like Bronchial Asthma, Bronchitis, Allergic Rhinitis, Sleep apnea & Sinusitis; Role of Yogic Diet on Respiratory Disorders
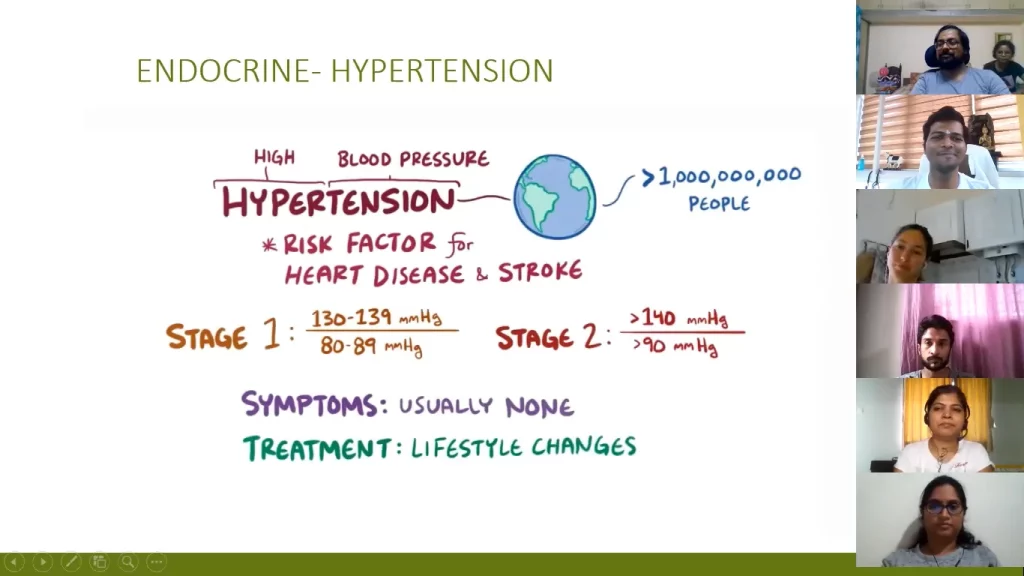
2.3 Role of Yoga practices on various Cardiovascular disorders like Hypertension, Atherosclerosis / Coronary artery disease, Angina pectoris / Myocardial Infarction ;Role of Yogic Diet on Cardiovascular disorders Role of Yogic Diet on Cardiovascular disorders.
2.4 Role of Yoga practices on various Neurological Disorder like Migraine, Headaches, Cerebrovascular accidents, Epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, Hearing impairment; Role of Yogic Diet on Neurological Disorder.
2.5 Role of Yoga practices on various Digestive and Excretory Disorders like Dyspepsia, Hyperacidity, Peptic Ulcers, Constipation, haemorrhoids and Irritable Bowel Syndrome; Role of Yogic Diet on Digestive and Excretory Disorders
2.6 Role of Yoga practices on various Obstetric & Gynecological Disorders like Menstrual Disorder(menstrual cramp, dysmenorrheal, pre-menstrual syndrome), Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS/PCOD), Pre-eclampsia or pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH),Menopausal discomfort (anxiety, irritability, insomnia, hot flashes.); Role of Yogic Diet on Obstetric & Gynecological Disorders
2.7 Role of Yoga practices on various Endocrine& Metabolic Disorders like Diabetes Mellitus, Thyroid Disorders, Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome; Role of Yogic Diet on Endocrine &Metabolic disorders.
2.8 Role of Yoga practices on various Psychological and Psychiatric Disorder like Obsessive Compulsive Disorder, Post-traumatic stress disorder, Depression, Anxiety, Schizophrenia, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Substance abuse; Role of Yogic Counseling Diet on Psychological and Psychiatric Disorder. YOG Certification Board 8
2.9 Role of Yoga practices on various old age problems like Spinal deformity, loss of coordination, imbalance, improper gait pattern, Stress, Alzheimer’s disease, Stress, Depression and reduction of all physiological function; Role of Yogic Diet in old age.
UNIT 3 Assessment Skill
3.1 Anthropometry measurements:-Weight, stature, eye height, Body Mass Index, Body Surface Area, Shoulder height, elbow height, head circumference, neck circumference, mid upper arm circumference, chest circumference, waist circumference, hip circumference, waist hip ratio, Measurement of fat percentage.
3.2 Physiological parameters and clinical examination: Knowledge of Clinical examination, heart rate, pulse rate and respiratory rate.
3.3 Knowledge of effect of Yogasana (lying, sitting, standing positions), suryanamaskar, Pranayama and Meditation on human body, Spirometry, knowledge of Reflexes, Measurement of strength of muscle. Measurement of flexibility. Recording of ECG, EEG, GSR and respiration.
3.4 Physical measurements:-Effects of exercise, cold stress and postural change on blood pressure and pulse rate, Measurement of strength and flexibility of muscle.
3.5 Understanding of muscles physiology with the help of model/chart and its practical applications in Asana.
3.6 Knowledge of COG, LOG, BOS in Asanas (in Sitting, standing, lying, balancing asanas) 3.7 Knowledge of Biomechanics of Yogic postures
Total Marks: 200 (Theory: 140+Practical: 60)
|
Theory
|
Practical
UNIT 1 Therapeutic Approch of Yoga Therapy in Classical Yogic Texts
Paramatman (Parmeshwar or Purushottam) as described in Bhagavadgita
and Bhakti Yoga in Bhagavadgita.
Bhagavadgita in day to day life.
1.2 Ashtang Yoga as a Therapy
1.3 Hatha Yoga as a Therapy
(SadhakTattva) of Hathyoga, Yama and Niyama.
1.4 Yoga Vashishtha
UNIT 2 Principals of Yoga Therapy
UNIT 3. Anatomy, Physiology and Psychology Foundations
3.1. MusculoSkeletal system :- Classification and function of bone and joints, types of muscles, structural organization of different type of muscles, knowledge of Neuro-muscular junction, Nerve –Muscle physiology, Mechanism of action potential, Electromyogram and muscle endurance, concept of haemostasis,
Mechanisms to maintain milieu environment. Positive and Negative Feedback mechanism.
UNIT 4 Yogic Concept for Management of Diseases
Yoga practice module for Musculo skeletal disorders: Precautions and Contra- indications of Yogic practices.
Yoga practice module for Respiratory disorders, Precautions and Contra- indications of Yogic practices
Yoga practice module for Cardiovascular disorders, Precautions and Contra- indications of Yogic practices.
Yoga practice module for Neurological Disorders; Precautions and Contra- indications of Yogic practices.
Yoga practice module for Obstetric & Gynaecological disorders; Precautions and Contra-indications of Yogic practices.
Yoga practice module for Obstetric & Gynaecological disorders; Precautions and Contra-indications of Yogic practices.
UNIT 1 Demonstration Skills
UNIT 6 Assessment Skills


Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I visited the yog centre and came back with a lot of inspiration enthusiasm and knowledge. It is a very good place for gaining yog experience knowledge and facts. Surely recommendedPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Today we had field visit to swasti yoga centre And we get to know more about the center and also about Dr Vikas Chothe and his contribution to spreading yoga all around World. It's so good to see the center and the coachPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Great people, geat place trying to make great yoga great again!Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Great experience...they are promoting yoga globally...🙌Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I liked the wall-clock very muchPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. शुभ सकाळ 😊 💫कर्म योग चे प्रतिबिंब स्वस्थ योग🙏💐Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. It's really good 👍🏻 It is One of the best Yoga centre In punePosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. It was wonderful experience to know more about yoga and how its creating awareness globally. Thank you 😊Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. It was a great experience visiting at swasti yoga centre. We got an inspiration to develop skill in the field of swasthavritta.Thankyou for the motivation.

Dr. Vikas Chothe
Swasti’s founder, Dr.Vikas Chothe, holds an MD, PhD in Ayurvedic medicine with Yoga Certification from AYUSH and QCI India. He has worked as a Yoga Ambassador for the government of India and is currently an examiner for YCB Yoga examination at TQ Cert (TATA projects) for the Yoga Certification Board. He has been working as a lead examiner since the beginning of the Yoga Certification Scheme in 2016 and has conducted exams for more than 3,000 students till date. Dr.Vikas has been invited by Indian Embassy Austria, Malaysia and Armenia and has visited USA, China, Malaysia, Italy and European countries for propagation of Yoga and Ayurveda. He is also yoga school auditor for the Yoga Certification Board (YCB) creating quality standards in yoga schools globally.

Dr. Shwetambari Vikas Chothe
Dr. Shwetambari Chothe is a Level 4 Yoga Master certified by Government of India, gold medalist in Masters in Yogashastra, consulting homeopath and co-founder of Swasti Yoga Center. Since childhood, she had a keen interest in yoga and Indian culture. She is a great chef with Ayurveda healthy cooking as her specialty. Qualifications: MD Homoeopath, Anatomy and Physiology expert, yoga teacher and practitioner for six years.
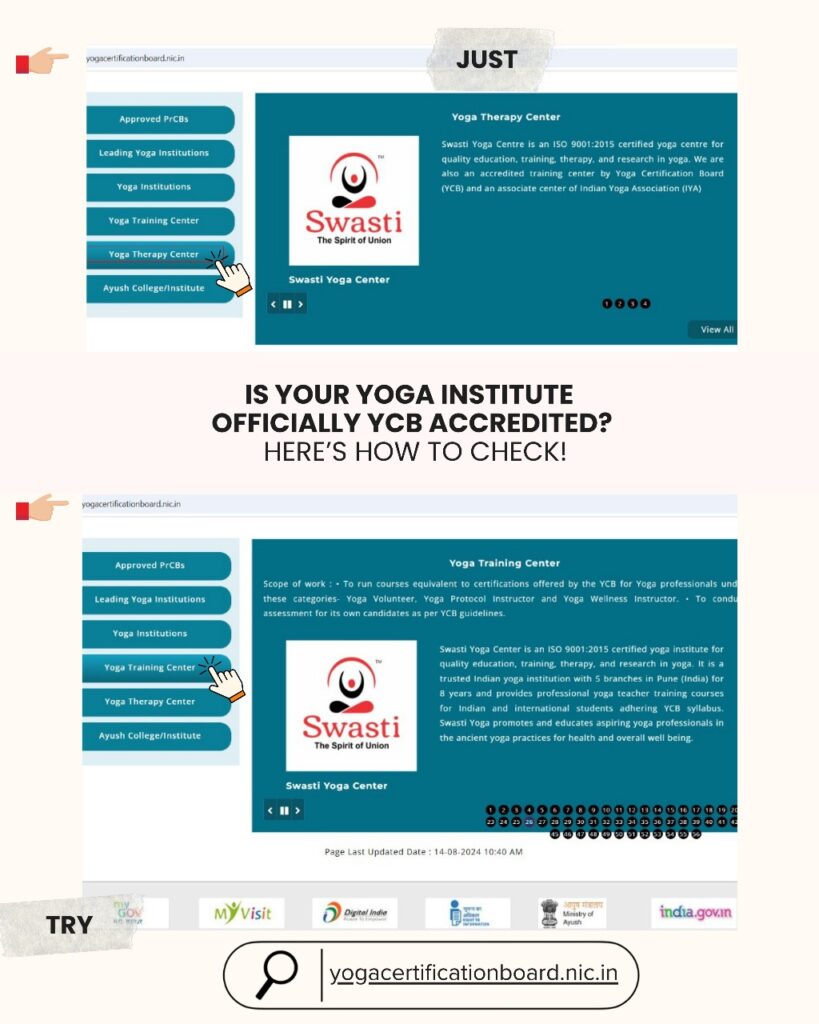
Before enrolling, ask three essential questions to confirm authenticity:
Is the institute officially accredited by the Yoga Certification Board (YCB) under the Ministry of AYUSH?
Are the trainers recognized YCB lead examiners, and how long have they been certified?
How many YCB exams has the institute conducted as lead examiners to show real experience?
These checks protect you from unrecognized institutes that misuse the YCB logo or make false claims.
How to verify accreditation:
Visit the official Yoga Certification Board website: https://yogacertificationboard.nic.in/, and under menu navigation, you will find YCB Certified -> Accredited Yoga Institution. Confirm the institute’s name under the list of accredited centers and examiners before enrolling.
Example –
The course fee depends on your location. For Indian students the fee is INR 60,000. For international students the fee is USD 1020, which includes the USD 450 Yoga Certification Board (YCB) assessment fee. Accommodation, food, yoga props charges are not included.
The Level 2 Yoga Therapy Course spans 12 months, comprising a total of 800 hours, with an estimated weekly commitment of 8–10 hours per week.
Yes. Swasti Yoga Center offers paid services of clean and comfortable rooms close to the campus in Pune. Accommodation is simple and peaceful — ideal for yoga practice. It’s not included in the Course fees. You can check available options on the Accommodation page.
All meals are pure vegetarian and sattvic. The food is freshly cooked, balanced, and supports your yoga routine. Learn more on the Yogic Food page.
Swasti regularly hosts students from many countries. The environment is safe, and the team ensures support for women and solo travelers. The campus is in a secure area, and staff are available for any local assistance you need.
Yes, international students usually need a tourist or student visa based on the course duration. After enrollment, Swasti guides you with your visa process. Learn more on the Admission page.
Yes. Swasti Yoga Center is certified by the Yoga Certification Board (YCB) under the Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India. You’ll receive an internationally recognized certificate after successful completion.
Yes. Study materials will be provided by Swasti Yoga Center.
To join the course, simply fill out the contact form on our website or get in touch with us directly.
You can call or WhatsApp us at +91-9922916025 / +91-8830079878, and our team will guide you through the next steps for enrollment and payment.
Subscribe Us
For Latest Update on Yoga in India and Worldwide
Swasti Yoga Center is a WHO-cited, Yoga Certification Board (YCB-IYA- AYUSH)-certified, and ISO 9001:2015 accredited Yoga Training and Therapy Institute, dedicated to delivering excellence in yoga education, therapy, training, and research.
Copyright © 2026 Swasti Yoga Center, India , All rights reserved.